Uric Acid Test Most Popular
The Uric Acid Test measures uric acid levels in blood to assess kidney function and detect gout, a form of arthritis caused by uric acid buildup. High levels may also signal kidney disease, kidney stones, or metabolic disorders, while low levels can occur with liver disease. Doctors use this test to investigate joint pain, swelling, or frequent urination, and to monitor treatment for gout, kidney stones, or chemotherapy-related complications.
- $47.01
- $19.95
- Save: 57.56%
The following is a list of what is included in the item above. Click the test(s) below to view what biomarkers are measured along with an explanation of what the biomarker is measuring.
Also known as: Serum Urate, UA
Uric Acid
The Uric Acid Test test contains 1 test with 1 biomarker .
Testing Method: Spectrophotometry
Collection Method: Blood Draw ![]()
Specimen: 1 mL SST Serum 
Test Preparation: No preparation required
When is a Uric Acid test ordered?
A Uric Acid test may be ordered in several situations to evaluate conditions related to uric acid levels:
-
Gout: Gout is a type of arthritis characterized by sudden and severe joint pain, swelling, and inflammation. A Uric Acid test helps in diagnosing gout by measuring the uric acid levels, as high levels can contribute to the development of gout.
-
Monitoring Uric Acid Levels: For individuals with a history of gout or kidney stones related to high uric acid levels, a Uric Acid test is performed to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and make necessary adjustments.
-
Assessing Kidney Function: Since the kidneys play a crucial role in excreting uric acid, a Uric Acid test may be ordered as part of a kidney function evaluation to assess how well the kidneys are processing and eliminating uric acid.
What does a Uric Acid blood test check for?
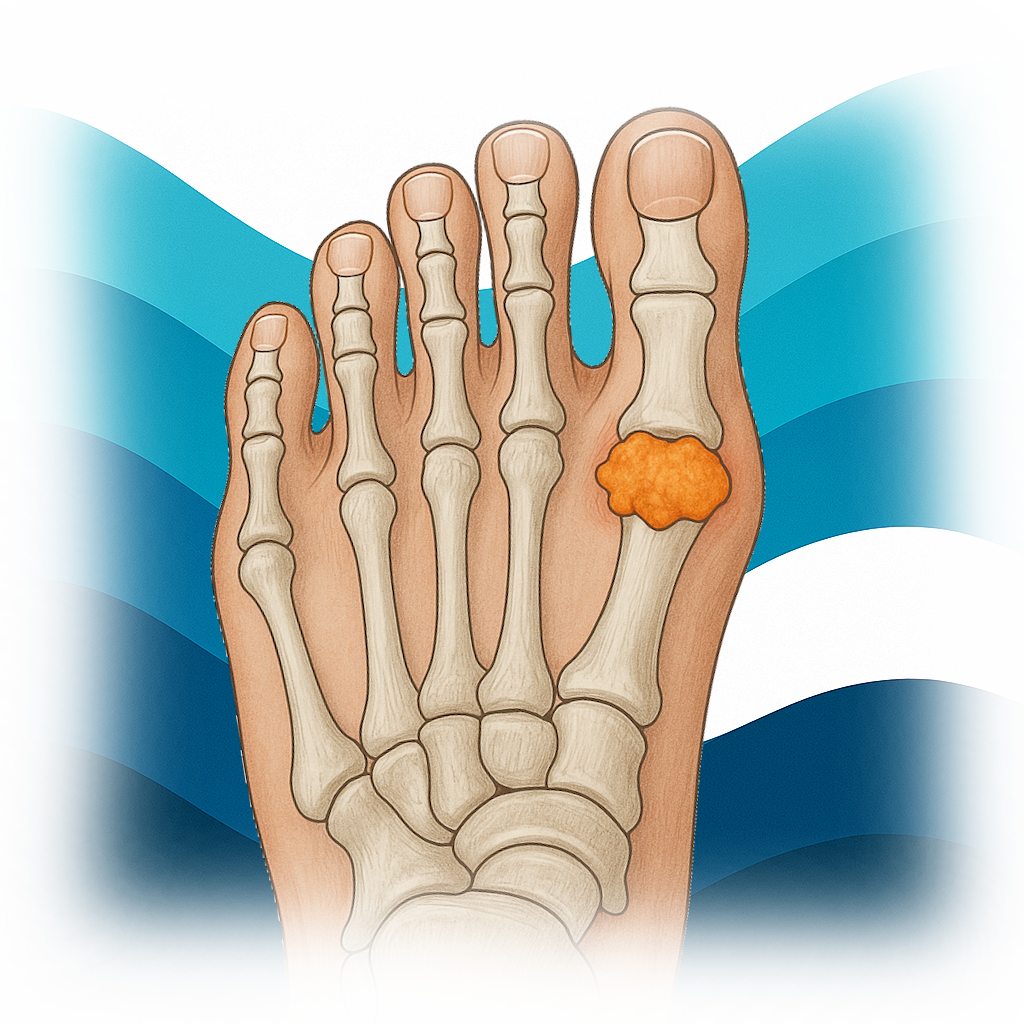 Purines are broken down to form uric acid. Purines are nitrogen-containing molecules that can be found in all of the body's cells, including DNA. This test determines how much uric acid is present in the blood or urine.
Purines are broken down to form uric acid. Purines are nitrogen-containing molecules that can be found in all of the body's cells, including DNA. This test determines how much uric acid is present in the blood or urine.
Cells break down as they age and die, releasing purines into the bloodstream. Purines can also be obtained through the digestion of specific foods, such as liver, anchovies, mackerel, dried beans and peas, and alcoholic beverages, particularly beer. The kidneys remove the majority of uric acid from the body, which is then excreted in the urine, with the remaining excreted in the stool.
When too much uric acid is created or not enough is eliminated from the body, it can build up in the body, causing blood levels to rise. Excess uric acid can induce gout, which is characterized by joint inflammation caused by the production of uric acid crystals in the joint fluid. Excess uric acid can also build up in tissues like the kidney, resulting in kidney stones or failure.
Too much uric acid in the body can occur as a result of creating too much, not removing enough, or a combination of both. Uric acid levels can rise as a result of an increase in cell death, as seen with some cancer treatments, or as a result of a rare hereditary tendency to make too much uric acid. Reduced uric acid removal is frequently caused by reduced renal function as a result of kidney disease.
Lab tests often ordered with a Uric Acid test:
When a Uric Acid test is ordered, several other tests may be performed to assess kidney function, rule out other causes of joint pain, or evaluate related health conditions. Here are some common tests ordered alongside a Uric Acid test:
-
- Purpose: To provide a broad overview of health and detect conditions such as anemia or infection.
- Why Is It Ordered: Although not directly related to uric acid levels, a CBC can help identify underlying health issues that may contribute to or be affected by elevated uric acid levels.
-
- Purpose: To evaluate how well the kidneys are working, as they play a crucial role in filtering uric acid from the blood.
- Why Is It Ordered: Kidney dysfunction can lead to an accumulation of uric acid, resulting in hyperuricemia and gout.
-
- Purpose: To measure the levels of key electrolytes in the blood.
- Why Is It Ordered: Electrolyte imbalances can be indicative of kidney problems or other health issues that might also affect uric acid levels.
-
- Purpose: To assess liver health, which can affect uric acid production and excretion.
- Why Is It Ordered: Liver diseases can impact uric acid levels and contribute to the development of gout.
-
C-Reactive Protein (CRP) and Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR):
- Purpose: Non-specific markers of inflammation.
- Why Is It Ordered: To assess for inflammation, which can be present in gout and other types of arthritis.
-
Calcium and Phosphorus:
- Purpose: To assess the levels of calcium and phosphorus, as abnormalities can be related to kidney stones and bone health.
- Why Is It Ordered: To rule out other causes of symptoms similar to gout, such as calcium-based kidney stones.
-
- Purpose: To examine the content of the urine.
- Why Is It Ordered: To check for the presence of uric acid crystals, signs of kidney disease, or to evaluate the risk of kidney stone formation.
-
- Purpose: To measure cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
- Why Is It Ordered: There is often an association between hyperuricemia, metabolic syndrome, and dyslipidemia.
-
Blood Glucose and Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c):
- Purpose: To assess blood sugar control and diagnose diabetes.
- Why Is It Ordered: Elevated uric acid levels are often associated with metabolic syndrome, which includes insulin resistance and diabetes.
These tests, along with a Uric Acid test, can help diagnose the cause of elevated uric acid levels, assess kidney function, and identify other related health issues. They are particularly important in the evaluation and management of gout but can also provide insights into other metabolic or systemic conditions. The specific tests chosen will depend on the individual's symptoms, medical history, and the results of the initial uric acid test.
Conditions where a Uric Acid test is recommended:
-
A Uric Acid test is commonly ordered for:
-
Gout: Gout is a form of arthritis caused by the deposition of urate crystals in the joints. Uric Acid tests help confirm the diagnosis by measuring elevated uric acid levels, which increase the risk of developing gout.
-
Kidney Stones: Uric acid stones are one type of kidney stones that form due to high uric acid levels in the urine. A Uric Acid test aids in identifying individuals at risk of developing uric acid stones.
How does my healthcare provider use a Uric Acid test?
Healthcare providers use the results of a Uric Acid test to:
-
Diagnose Gout: Elevated uric acid levels can indicate the presence of gout or an increased risk of developing gout. The test helps confirm the diagnosis and guide appropriate treatment strategies.
-
Monitor Treatment Response: For individuals receiving treatment for gout or conditions related to high uric acid levels, periodic Uric Acid tests are performed to assess the effectiveness of treatment and make necessary adjustments to medication or lifestyle modifications.
-
Evaluate Kidney Function: Since the kidneys play a crucial role in excreting uric acid, a Uric Acid test helps healthcare providers assess kidney function and identify any underlying kidney-related issues contributing to elevated uric acid levels.
What does my Uric Acid result mean?
Hyperuricemia is defined as blood uric acid levels that are higher than usual. It can be caused by the body creating too much uric acid or the kidneys failing to eliminate enough uric acid from the body. To determine the reason of uric acid overproduction or reduced elimination, more research is needed.
Purine break-down is affected by a number of genetic inborn defects. Increased uric acid production can be caused by cancer that has spread from its original place, leukemias, multiple myeloma, and cancer chemotherapy. Reduced uric acid elimination can be caused by chronic renal illness, acidosis, pregnancy toxemia, and alcoholism.
Increased uric acid levels can cause crystals to develop in the joints, resulting in the joint inflammation and pain associated with gout. Uric acid can form crystals or kidney stones, which can cause kidney injury.
Low uric acid levels in the blood are significantly less common than high ones, and they are rarely a cause for concern. Although low uric acid levels have been linked to liver and renal disease, Fanconi syndrome, toxic exposure, and in rare cases, a hereditary metabolic deficiency, these problems are usually detected by other tests and symptoms rather than a single low uric acid result.
Most Common Questions About the Uric Acid test:
Understanding the Test
What is the Uric Acid test?
The Uric Acid test is a blood or urine test that measures the levels of uric acid in your body. Uric acid is a chemical produced when the body breaks down substances called purines, which are found in some foods and drinks and are also produced by the body.
Why is the Uric Acid test done?
The Uric Acid test is usually done to help diagnose gout, a type of arthritis caused by too much uric acid in the body. It can also help evaluate the cause of kidney stones and monitor the progress of treatments for conditions that can cause high uric acid levels.
Interpreting the Results
What does a high uric acid level indicate in the Uric Acid test?
A high uric acid level may suggest that you have gout or kidney stones. It could also mean that you have a condition that affects how the body processes uric acid or purines, such as leukemia or kidney disease.
What does a low uric acid level indicate in the Uric Acid test?
A low uric acid level is less common but could indicate kidney disease, exposure to lead, or a rare inherited disorder called Wilson's disease. Certain drugs, like allopurinol and probenecid, which are used to treat gout, can also lower uric acid levels.
About the Test
Can certain medications affect the results of the Uric Acid test?
Yes, certain medications can affect the results of the Uric Acid test. These include drugs used to treat gout, chemotherapy drugs, diuretics, and drugs containing salicylates, among others. It's important to inform your healthcare provider of all medications you're taking.
What factors can influence the results of the Uric Acid test?
Factors that can influence the Uric Acid test results include your diet, alcohol intake, how much you exercise, and whether you're dehydrated. Certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease, hypothyroidism, and psoriasis, can also affect uric acid levels.
Understanding the Implications
What role does uric acid play in the body, as assessed by the Uric Acid test?
Uric acid is a waste product produced when the body breaks down purines. Normally, uric acid is dissolved in the blood and passed out of the body in urine. If too much uric acid is produced or not enough is excreted, it can build up and form crystals that can cause gout or kidney stones.
Can the Uric Acid test give insight into my overall metabolic health?
Yes, the Uric Acid test can provide insights into metabolic health. High levels of uric acid can indicate metabolic syndrome, a group of conditions that increase your risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes.
Risks and Precautions
Are there risks associated with having high or low uric acid levels as indicated by the Uric Acid test?
Yes, high uric acid levels can lead to painful conditions like gout and kidney stones. Over time, high uric acid levels can also cause kidney disease. Low uric acid levels, while less common, can indicate conditions such as kidney disease or Wilson's disease.
Can the Uric Acid test provide insight into my risk of developing certain diseases?
Yes, the Uric Acid test can indicate your risk of diseases such as gout, kidney stones, and kidney disease. High uric acid levels can also be associated with an increased risk of heart disease and stroke.
Dealing with Abnormal Results
What should I do if my Uric Acid test shows high or low levels of uric acid?
If your Uric Acid test shows high or low levels, it's important to talk to your healthcare provider for further evaluation. The treatment will depend on the underlying cause of the abnormal uric acid levels.
Are there ways to manage high or low uric acid levels as identified in the Uric Acid test?
Yes, high uric acid levels can often be managed with medications and lifestyle changes like a healthier diet, regular exercise, and limiting alcohol intake. Low uric acid levels may need to be managed by treating the underlying cause.
Interpreting the Test Results
How are the results of the Uric Acid test interpreted?
Uric Acid test results are interpreted by comparing your levels with normal ranges. These ranges can vary among different labs, but generally, normal levels are 2.4-6.0 mg/dL for women and 3.4-7.0 mg/dL for men.
Understanding the Test with Other Conditions
How does the Uric Acid test relate to the diagnosis of gout?
The Uric Acid test is a key tool in diagnosing gout. High levels of uric acid in the bloodcan lead to the formation of uric acid crystals in the joints, which causes the pain and inflammation characteristic of gout.
Can the Uric Acid test provide information about my kidney health?
Yes, high levels of uric acid in the urine, as measured by a urinary Uric Acid test, can indicate that your kidneys are not properly removing waste. This could suggest kidney disease.
Is the Uric Acid test used in the management of certain types of cancer, like leukemia or lymphoma?
Yes, the Uric Acid test can be used in the management of certain types of cancer. Some cancer treatments cause rapid death of tumor cells, which can lead to high levels of uric acid in the blood, a condition known as tumor lysis syndrome.
Role of Diet and Lifestyle
Can my diet affect the results of the Uric Acid test?
Yes, your diet can significantly influence your uric acid levels. Consuming foods and drinks high in purines, like red meat, seafood, and alcohol, can lead to higher uric acid levels.
Can lifestyle changes help manage high uric acid levels as indicated by the Uric Acid test?
Yes, lifestyle changes like eating a low-purine diet, limiting alcohol, staying hydrated, losing weight if overweight, and exercising regularly can help manage high uric acid levels.
Uric Acid in Different Populations
Do uric acid levels vary by sex, as measured by the Uric Acid test?
Yes, men generally have higher uric acid levels than women until women reach menopause. After menopause, women's uric acid levels approach those of men.
How do uric acid levels change with age as measured by the Uric Acid test?
Uric acid levels can increase with age. However, extremely high levels are usually not due to aging alone and may indicate a medical condition or the need for a medication review.
The Importance of Discussion with a Healthcare Provider
What should I discuss with my healthcare provider before getting the Uric Acid test?
Before getting the Uric Acid test, you should discuss your medical history, any symptoms you've been experiencing, and any medications you're currently taking. This information will help your healthcare provider interpret your test results in the context of your overall health and lifestyle.
What questions should I ask my healthcare provider after getting the Uric Acid test?
After getting the Uric Acid test, you might ask your healthcare provider about the meaning of your results, whether you need additional tests, and if you should make any lifestyle changes or start a treatment plan.
Future Considerations
How often should the Uric Acid test be repeated?
The frequency of Uric Acid testing depends on your health condition. If you have gout, kidney stones, or a related health issue, your doctor may recommend regular monitoring. Always follow your healthcare provider's advice on test frequency.
What future medical tests might be needed if the Uric Acid test reveals abnormal levels?
If your Uric Acid test results are abnormal, further investigations may be needed to identify the underlying cause. These could include kidney function tests, liver function tests, blood glucose tests, and lipid profile tests, among others.
General
Can the Uric Acid test tell me about my risk of heart disease?
Elevated uric acid levels can be a risk factor for heart disease. Some studies have found an association between high uric acid levels and conditions like hypertension, coronary artery disease, and heart failure. However, more research is needed to fully understand this relationship. If you have high uric acid levels, it's important to discuss this risk with your healthcare provider.
We advise having your results reviewed by a licensed medical healthcare professional for proper interpretation of your results.
